You must have come across the terms “Binning” and “Silicon Lottery” while watching or browsing about CPUs and Graphics cards. You could have also come across them when you try to overclock your CPUs and Graphics cards. This article will give you a clear picture of what is Binning and What is silicon lottery.
Before you understand what binning and silicon lottery is, you need to understand how CPUs and GPUs are made.
CPUs are made up of silicon. Silicon is first purified and then cut into wafers. The wafers are fitted with hundreds of CPU dies containing transistors after many fabrication/Lithographic processes.
There will be variations in the quality of CPUs spread across the wafer due to errors being introduced to them when being subjected to various processes during their manufacture. This is where binning comes into play.
What is Binning
Binning is a process through which manufacturers of CPUs, GPUs, and RAMs categorize them according to their build quality and performance.
Every single CPU, GPU, and RAM that is manufactured will need to adhere to a specific standard of performance in voltage, power consumption, clock speed, heat output, etc. set by the manufacturer.
These standards vary depending upon the architecture of the components. Not all of them satisfy those standards due to the complexity and errors involved in their manufacturing process.
These components are divided according to the results of the test of their standards and placed into various “Bins”. If a component satisfies all the standards, it will be placed in a bin containing good quality components. Same in the case of components that do not satisfy the standards. They will be placed in bins having components of lesser quality. These components are often sold at various prices due to the differences in their quality which affects performance.
For example, consider AMD’s Ryzen 3, Ryzen 5, and Ryzen 7 processors. AMD has set few standards like defined clock speed, a certain number of cores, defined voltage, TDP, etc for Ryzen 5 processors. If any CPU fails to adhere to these standards, it will be binned as a Ryzen 3 processor. If it satisfies their standards, it will be binned as Ryzen 5 processors. If it exceeds their standards and meets the standards set to a Ryzen 7 processor, it will be binned as a Ryzen 7 processor.
So, if you’re using a Ryzen 3 processor, it could have been a Ryzen 5 but it couldn’t meet the manufacturer’s expectations.
Binning among processors of the same model is also common. For example, the highest quality binned i7s will be sold as an unlocked “K-series” processors. They have more clock speed and produce less heat. You will be able to overclock them efficiently than their locked counterparts. So, the i7-7700K is binned higher than an ordinary i7-7700.

The Binning process is also used for sorting graphics cards. They will also be binned according to the standards set by their manufacturers. It is not uncommon to see different graphics cards running on the same GPU. They will have different clock speeds, different power consumption values, different cores, etc. due to binning.
For example, GP104 is the GPU used in GTX 1070, GTX 1070 Ti, and GTX 1080. The GTX 1080 will have more number of cores available working at a higher clock speed than the GTX 1070. The GTX 1070 could have become a GTX 1080 if it could have met the manufacturer’s expectations.
Binning among graphics cards of the same model is also common. You might have noticed the same graphics card being sold at different clock speeds at different prices. Though they are manufactured in the same way, they will have differences in their performance due to the minute complexities involved in their manufacturing process.
For example, a GTX 1080 Xtreme gaming OC will be more expensive than a GTX 1080. The former has higher clock speed and offers more performance. Hence it will be binned higher than the latter.

You might think you could enable the disabled cores on your CPUs and GPUs and make them function on par with highly binned components. It was possible many years ago through bios tricks, firmware updates, etc. but these days the manufacturers physically disable to connections between inefficient (or inactive) cores and the rest of the processors. So, they cannot be used at all by consumers.
What is Silicon Lottery
As I’ve told you earlier, CPU, RAMs, GPUs will be sorted and binned according to their performance and quality.
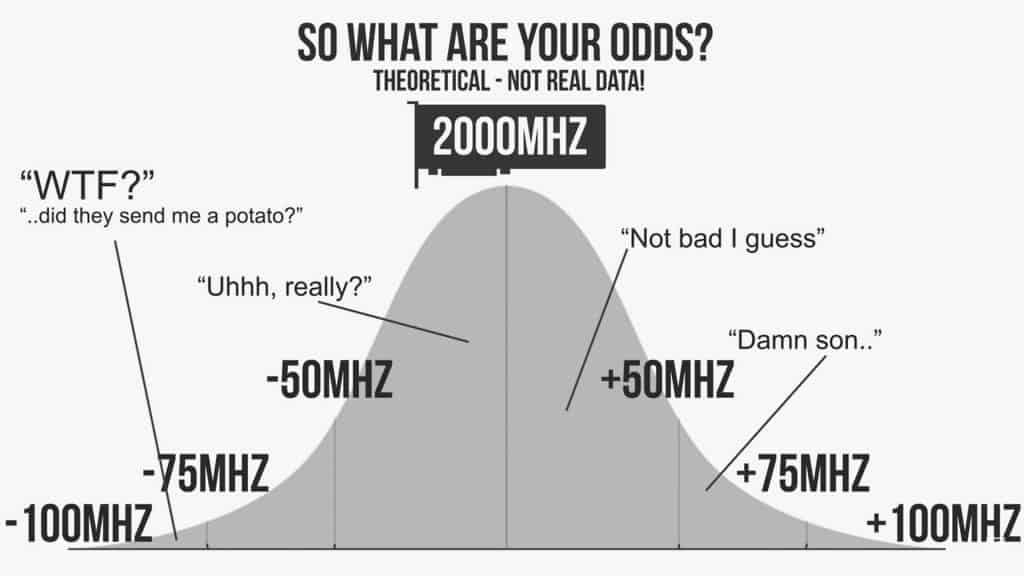
If you pick two identical CPUs or GPUs from the same bin and compare their overclocking performance, both of them will not be exactly equal in their performance even though they are of the same model. One will perform slightly better than the other. This is called the silicon lottery.
This happens because of the minute complexities involved in the manufacturing of these components. Their performance will not precisely hit the mark of the manufacturer’s expectations. It will vary by a small value.
For example, when you and your friend buy a GTX 1080 Xtreme graphics card, you can be sure that you and your friend is buying a higher binned graphics card. But when you try overclocking them, both of you will be able to overclock it to different extents. This is because of the silicon lottery.

If you could overclock it better than your friend, it means you have won the silicon lottery. You have a slightly better card than your friend even though you both paid the same price for it.
The same can be said for CPUs as well. Let’s say both you and your friend bought an unlocked i7-7700K CPU. When you try overclocking them, you and your friend will have different results in overclocking even though they are from a higher binned set of CPUs. This happens because of the minute complexities involved in CPU manufacturing.

It is called a lottery because you are in for a game of chance. You may or may not hit the lottery.
Also, there is not much to lose if you did not win the lottery. Though the gains and losses are noticeable, they’re not a tipping point.
In the case of CPUs, the extra gain you get by maximum overclock can range between 0.1GHz to 0.3GHz. It will be 0.5Ghz if you’re extremely lucky.
In the case of Graphics cards, they may range between +/- 50Mhz in most cases. If you could boost the clock speeds more than 75MHz, consider yourself lucky.